2023-08-08:給你一棵 n 個節點的樹(連通無向無環的圖)
<dfn id='x13cp'><optgroup id='x13cp'></optgroup></dfn><tfoot id='x13cp'><bdo id='x13cp'><div id='x13cp'></div><i id='x13cp'><dt id='x13cp'></dt></i></bdo></tfoot> 節點編號從 0 到 n - 1 且恰好有 n - 1 條邊
給你一個長度為 n 下標從 0 開始的整數數組 vals
分別表示每個節點的值
同時給你一個二維整數數組 edges
其中 edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示節點 ai 和 bi 之間有一條 無向 邊
一條 好路徑 需要滿足以下條件:
開始節點和結束節點的值 相同 。
開始節點和結束節點中間的所有節點值都 小于等于 開始節點的值。
(也就是說開始節點的值應該是路徑上所有節點的最大值)。
請你返回不同好路徑的數目。
注意,一條路徑和它反向的路徑算作 同一 路徑。
比方說, 0 -> 1 與 1 -> 0 視為同一條路徑。單個節點也視為一條合法路徑。
輸入:vals = [1,1,2,2,3], edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[2,4]]。
輸出:7。
來自谷歌。
來自[左神](//b23.tv/Zho7gh0)
答案2023-08-08:
# 大致的步驟如下:
1.創建一個圖(樹)數據結構,并初始化節點的值和連接關系。
2.對節點的值進行排序,按照值的大小順序處理節點。
3.初始化并查集,用于管理節點的連通性。
4.創建一個數組記錄每個連通分量中值最大的節點的索引。
5.創建一個數組記錄每個連通分量中值最大的節點所在連通分量的節點數。
6.初始化答案為節點的總數。
7.遍歷排序后的節點列表,依次處理每個節點:
7.1.獲取當前節點的索引和值。
7.2.查找當前節點的連通分量代表節點。
7.3.查找當前連通分量代表節點的最大值節點的索引。
7.4.遍歷當前節點的鄰居節點,將鄰居節點的值與當前節點值進行比較。
7.5.若鄰居節點的值小于等于當前節點值,并且鄰居節點所在的連通分量與當前連通分量不同,則進行以下操作:
7.5.1.查找鄰居節點連通分量的代表節點的最大值節點的索引。
7.5.2.若鄰居節點的值等于該最大值節點的值,則更新答案并累加該最大值節點所在連通分量的節點數。
7.5.3.合并當前節點和鄰居節點所在的連通分量。
7.5.4.更新當前連通分量代表節點的索引。
8.返回答案。
時間復雜度為O(nlogn)。
空間復雜度為O(n)。
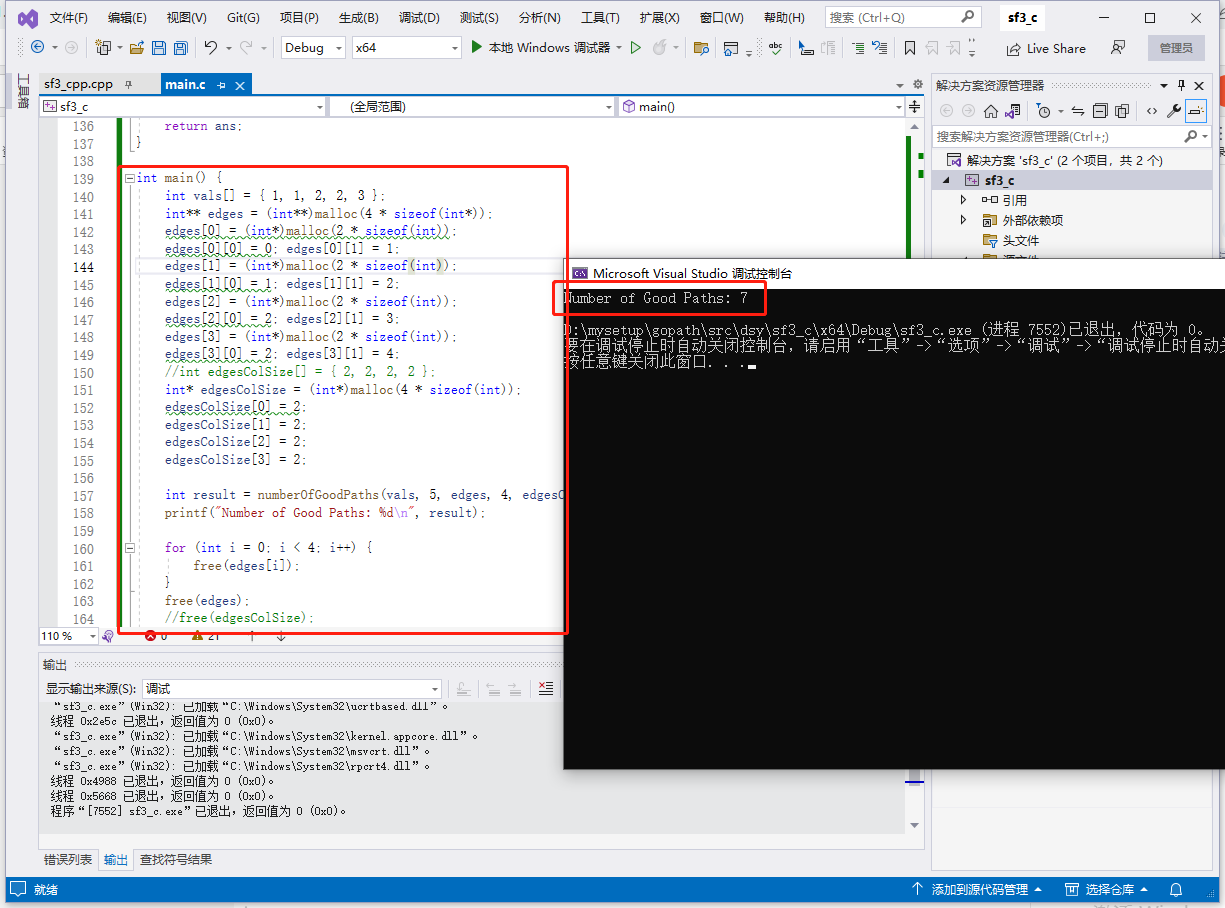
# go完整代碼如下:
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sort"
)
func numberOfGoodPaths(vals []int, edges [][]int) int {
n := len(vals)
graph := make([][]int, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
graph[i] = make([]int, 0)
}
for _, e := range edges {
graph[e[0]] = append(graph[e[0]], e[1])
graph[e[1]] = append(graph[e[1]], e[0])
}
nodes := make([][]int, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
nodes[i] = make([]int, 2)
nodes[i][0] = i
nodes[i][1] = vals[i]
}
sort.Slice(nodes, func(i, j int) bool {
return nodes[i][1] < nodes[j][1]
})
uf := NewUnionFind(n)
maxIndex := make([]int, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
maxIndex[i] = i
}
maxCnts := make([]int, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
maxCnts[i] = 1
}
ans := n
for _, node := range nodes {
curi := node[0]
curv := vals[curi]
curCandidate := uf.Find(curi)
curMaxIndex := maxIndex[curCandidate]
for _, nexti := range graph[curi] {
nextv := vals[nexti]
nextCandidate := uf.Find(nexti)
if curCandidate != nextCandidate && curv >= nextv {
nextMaxIndex := maxIndex[nextCandidate]
if curv == vals[nextMaxIndex] {
ans += maxCnts[curMaxIndex] * maxCnts[nextMaxIndex]
maxCnts[curMaxIndex] += maxCnts[nextMaxIndex]
}
candidate := uf.Union(curi, nexti)
maxIndex[candidate] = curMaxIndex
}
}
}
return ans
}
type UnionFind struct {
parent []int
size []int
help []int
}
func NewUnionFind(n int) *UnionFind {
uf := &UnionFind{
parent: make([]int, n),
size: make([]int, n),
help: make([]int, n),
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
uf.parent[i] = i
uf.size[i] = 1
}
return uf
}
func (uf *UnionFind) Find(i int) int {
hi := 0
for i != uf.parent[i] {
uf.help[hi] = i
hi++
i = uf.parent[i]
}
for hi--; hi >= 0; hi-- {
uf.parent[uf.help[hi]] = i
}
return i
}
func (uf *UnionFind) Union(i, j int) int {
f1 := uf.Find(i)
f2 := uf.Find(j)
if f1 != f2 {
if uf.size[f1] >= uf.size[f2] {
uf.size[f1] += uf.size[f2]
uf.parent[f2] = f1
return f1
} else {
uf.size[f2] += uf.size[f1]
uf.parent[f1] = f2
return f2
}
}
return f1
}
func main() {
vals := []int{1, 1, 2, 2, 3}
edges := [][]int{{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}}
result := numberOfGoodPaths(vals, edges)
fmt.Println(result)
}
```
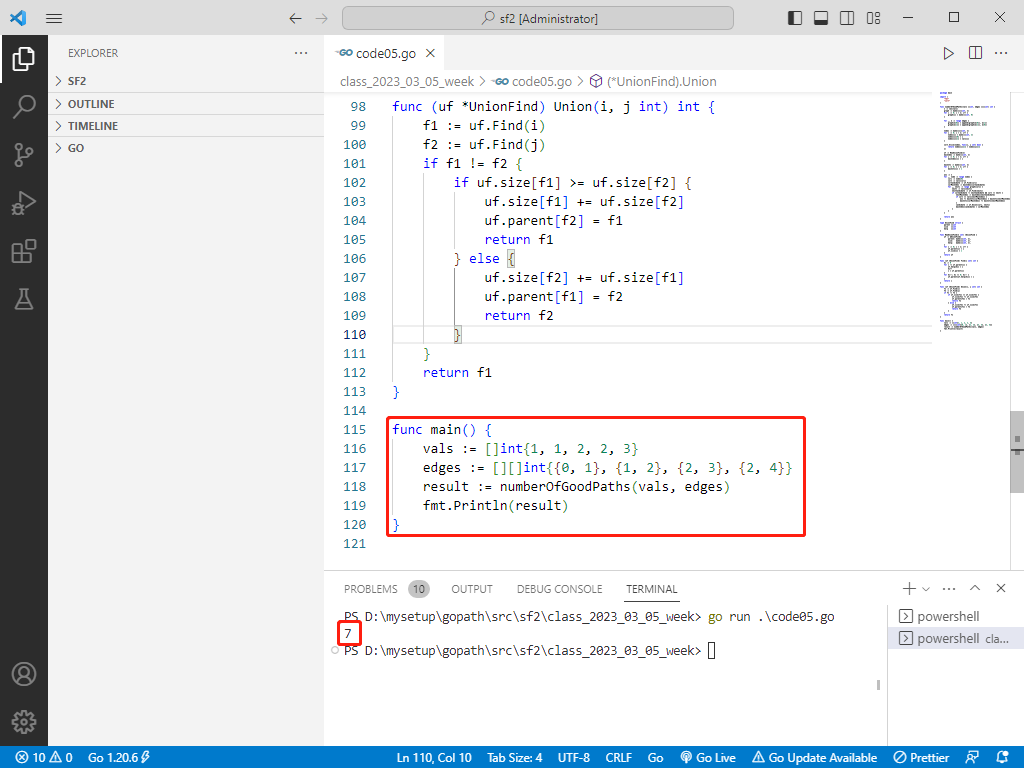
# rust完整代碼如下:
```rust
use std::cmp::Ordering;
fn number_of_good_paths(vals: Vec<i32>, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let n = vals.len();
let mut graph: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![Vec::new(); n];
for edge in edges {
let a = edge[0] as i32;
let b = edge[1] as i32;
graph[a as usize].push(b);
graph[b as usize].push(a);
}
let mut nodes: Vec<[i32; 2]> = vals
.iter()
.enumerate()
.map(|(i, &v)| [i as i32, v as i32])
.collect();
nodes.sort_by(|a, b| a[1].cmp(&b[1]));
let mut uf = UnionFind::new(n as i32);
let mut max_index: Vec<i32> = (0..n as i32).collect();
let mut max_counts: Vec<i32> = vec![1; n];
let mut ans = n as i32;
for node in nodes {
let cur_i = node[0];
let cur_v = vals[cur_i as usize];
let cur_candidate = uf.find(cur_i);
let cur_max_index = max_index[cur_candidate as usize];
for &next_i in &graph[cur_i as usize] {
let next_v = vals[next_i as usize];
let next_candidate = uf.find(next_i);
if cur_candidate != next_candidate && cur_v >= next_v {
let next_max_index = max_index[next_candidate as usize];
if cur_v == vals[next_max_index as usize] {
ans += max_counts[cur_max_index as usize] * max_counts[next_max_index as usize];
max_counts[cur_max_index as usize] += max_counts[next_max_index as usize];
}
let candidate = uf.union(cur_i, next_i);
max_index[candidate as usize] = cur_max_index;
}
}
}
ans
}
struct UnionFind {
parent: Vec<i32>,
size: Vec<i32>,
help: Vec<i32>,
}
impl UnionFind {
fn new(n: i32) -> UnionFind {
UnionFind {
parent: (0..n).collect(),
size: vec![1; n as usize],
help: Vec::new(),
}
}
fn find(&mut self, i: i32) -> i32 {
let mut hi = 0;
let mut x = i;
while x != self.parent[x as usize] {
self.help.push(x);
x = self.parent[x as usize];
hi += 1;
}
for hi in (0..hi).rev() {
self.parent[self.help[hi as usize] as usize] = x;
}
self.help.clear();
x
}
fn union(&mut self, i: i32, j: i32) -> i32 {
let f1 = self.find(i);
let f2 = self.find(j);
if f1 != f2 {
if self.size[f1 as usize] >= self.size[f2 as usize] {
self.size[f1 as usize] += self.size[f2 as usize];
self.parent[f2 as usize] = f1;
return f1;
} else {
self.size[f2 as usize] += self.size[f1 as usize];
self.parent[f1 as usize] = f2;
return f2;
}
}
f1
}
}
fn main() {
let vals = vec![1, 1, 2, 2, 3];
let edges = vec![vec![0, 1], vec![1, 2], vec![2, 3], vec![2, 4]];
let result = number_of_good_paths(vals, edges);
println!("Number of good paths: {}", result);
}
```
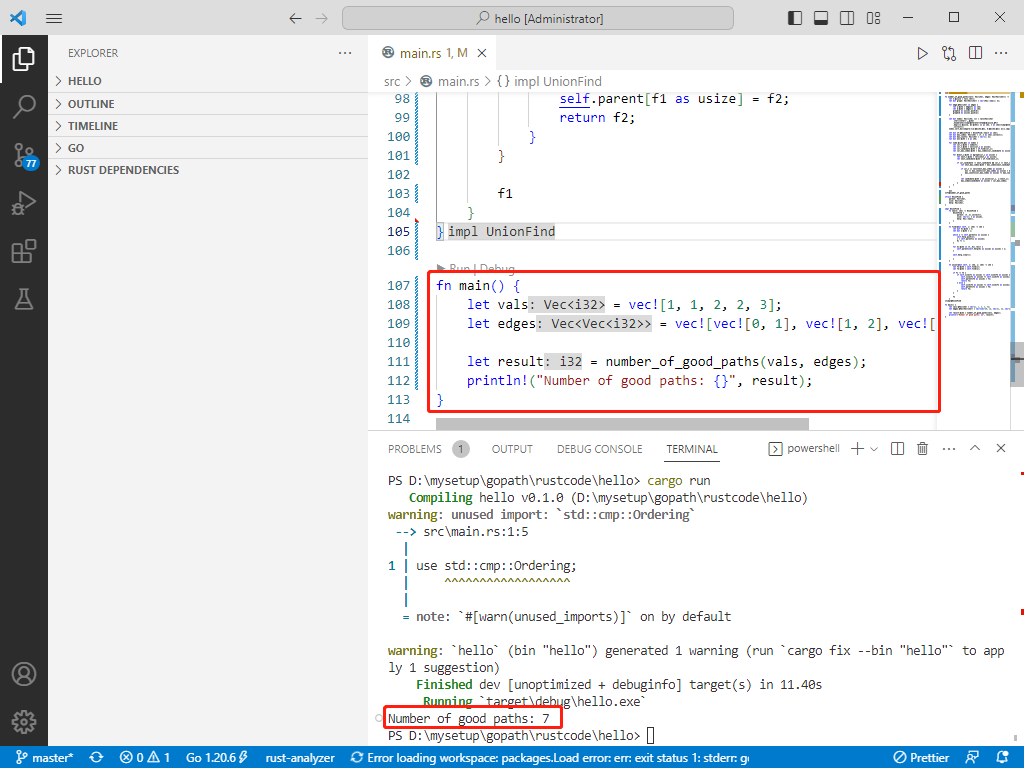
# c++完整代碼如下:
```cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int numberOfGoodPaths(vector<int>& vals, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int n = vals.size();
// Build the graph
vector<vector<int>> graph(n);
for (auto& edge : edges) {
int a = edge[0];
int b = edge[1];
graph[a].push_back(b);
graph[b].push_back(a);
}
// Sort the nodes based on values
vector<pair<int, int>> nodes;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
nodes.push_back({ vals[i], i });
}
sort(nodes.begin(), nodes.end());
vector<int> parent(n);
vector<int> size(n, 1);
vector<int> maxIndex(n);
vector<int> maxCnts(n, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
maxIndex[i] = i;
}
int ans = n;
// Traverse the nodes in ascending order of values
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int curi = nodes[i].second;
int curv = vals[curi];
int curCandidate = parent[curi];
int curMaxIndex = maxIndex[curCandidate];
// Iterate over the neighbors
for (int nexti : graph[curi]) {
int nextv = vals[nexti];
int nextCandidate = parent[nexti];
if (curCandidate != nextCandidate && curv >= nextv) {
int nextMaxIndex = maxIndex[nextCandidate];
if (curv == vals[nextMaxIndex]) {
ans += maxCnts[curMaxIndex] * maxCnts[nextMaxIndex];
maxCnts[curMaxIndex] += maxCnts[nextMaxIndex];
}
int candidate = parent[curi] = parent[nexti] = curMaxIndex;
maxIndex[candidate] = curMaxIndex;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
vector<int> vals = { 1, 1, 2, 2, 3 };
vector<vector<int>> edges = { {0, 1}, {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 4} };
int result = numberOfGoodPaths(vals, edges);
cout << "Number of Good Paths: " << result << endl;
return 0;
}
```
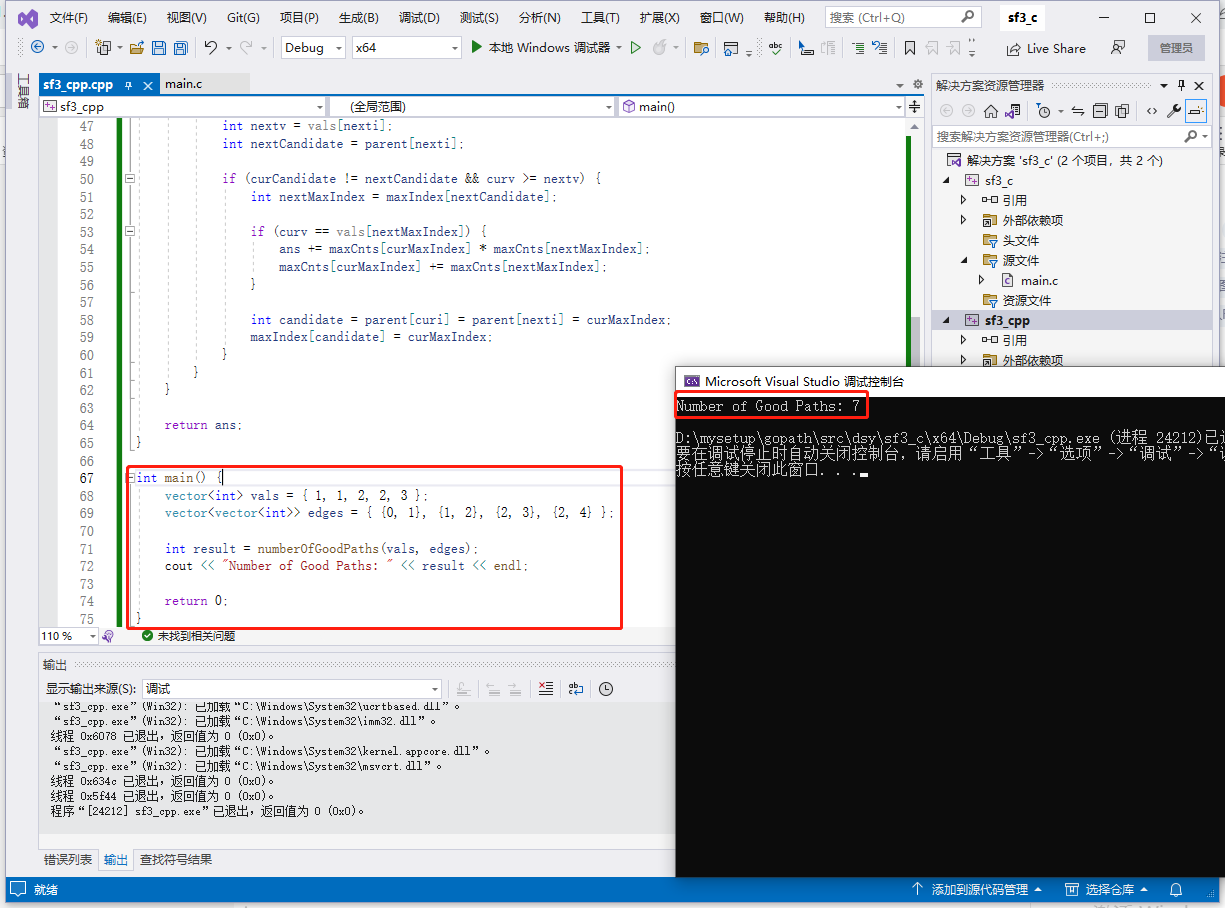
# c完整代碼如下:
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct UnionFind {
int* parent;
int* size;
int* help;
};
struct UnionFind* createUnionFind(int n) {
struct UnionFind* uf = (struct UnionFind*)malloc(sizeof(struct UnionFind));
uf->parent = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
uf->size = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
uf->help = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
uf->parent[i] = i;
uf->size[i] = 1;
}
return uf;
}
int find(struct UnionFind* uf, int i) {
int hi = 0;
while (i != uf->parent[i]) {
uf->help[hi++] = i;
i = uf->parent[i];
}
for (hi--; hi >= 0; hi--) {
uf->parent[uf->help[hi]] = i;
}
return i;
}
int unionSet(struct UnionFind* uf, int i, int j) {
int f1 = find(uf, i);
int f2 = find(uf, j);
if (f1 != f2) {
if (uf->size[f1] >= uf->size[f2]) {
uf->size[f1] += uf->size[f2];
uf->parent[f2] = f1;
return f1;
}
else {
uf->size[f2] += uf->size[f1];
uf->parent[f1] = f2;
return f2;
}
}
return f1;
}
// Comparison function for qsort
int compare(const void* a, const void* b) {
int* na = *(int**)a;
int* nb = *(int**)b;
return na[1] - nb[1];
}
int numberOfGoodPaths(int* vals, int valsSize, int** edges, int edgesSize, int* edgesColSize) {
int n = valsSize;
int i, j;
// 創建圖
int** graph = (int**)malloc(n * sizeof(int*));
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
edgesColSize[i] = 0;
}
for (i = 0; i < edgesSize; i++) {
int u = edges[i][0];
int v = edges[i][1];
graph[u][edgesColSize[u]++] = v;
graph[v][edgesColSize[v]++] = u;
}
// 創建節點數組
int** nodes = (int**)malloc(n * sizeof(int*));
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
nodes[i] = (int*)malloc(2 * sizeof(int));
nodes[i][0] = i;
nodes[i][1] = vals[i];
}
// 根據節點值排序
qsort(nodes, n, sizeof(nodes[0]),compare);
// 創建并初始化并查集
struct UnionFind* uf = createUnionFind(n);
int* maxIndex = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
int* maxCnts = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
maxIndex[i] = i;
maxCnts[i] = 1;
}
int ans = n;
// 遍歷節點
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int curi = nodes[i][0];
int curv = vals[curi];
int curCandidate = find(uf, curi);
int curMaxIndex = maxIndex[curCandidate];
// 遍歷鄰居
for (j = 0; j < edgesColSize[curi]; j++) {
int nexti = graph[curi][j];
int nextv = vals[nexti];
int nextCandidate = find(uf, nexti);
if (curCandidate != nextCandidate && curv >= nextv) {
int nextMaxIndex = maxIndex[nextCandidate];
if (curv == vals[nextMaxIndex]) {
ans += maxCnts[curMaxIndex] * maxCnts[nextMaxIndex];
maxCnts[curMaxIndex] += maxCnts[nextMaxIndex];
}
int candidate = unionSet(uf, curi, nexti);
maxIndex[candidate] = curMaxIndex;
}
}
}
// 釋放內存
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
free(graph[i]);
free(nodes[i]);
}
free(graph);
free(nodes);
free(maxIndex);
free(maxCnts);
free(uf->parent);
free(uf->size);
free(uf->help);
free(uf);
return ans;
}
int main() {
int vals[] = { 1, 1, 2, 2, 3 };
int** edges = (int**)malloc(4 * sizeof(int*));
edges[0] = (int*)malloc(2 * sizeof(int));
edges[0][0] = 0; edges[0][1] = 1;
edges[1] = (int*)malloc(2 * sizeof(int));
edges[1][0] = 1; edges[1][1] = 2;
edges[2] = (int*)malloc(2 * sizeof(int));
edges[2][0] = 2; edges[2][1] = 3;
edges[3] = (int*)malloc(2 * sizeof(int));
edges[3][0] = 2; edges[3][1] = 4;
//int edgesColSize[] = { 2, 2, 2, 2 };
int* edgesColSize = (int*)malloc(4 * sizeof(int));
edgesColSize[0] = 2;
edgesColSize[1] = 2;
edgesColSize[2] = 2;
edgesColSize[3] = 2;
int result = numberOfGoodPaths(vals, 5, edges, 4, edgesColSize);
printf("Number of Good Paths: %d\n", result);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
free(edges[i]);
}
free(edges);
//free(edgesColSize);
return 0;
}
```